HBOT Chambers
Also known as Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy chambers or Hyperbaric chambers for Oxygen treatment. There are three types:
Monoblock single place chamber
Build and approved for one single person at a time. These chambers can be pressurized by medical …
Read Moreoxygen or conventional indoor air. If pressurized with 100% oxygen, the patient breathes oxygen directly while receiving care.

If pressurized by conventional air, the patient will breathe 100% oxygen through the breathing mask. Each patient is uniquely assigned a specific atmospheric pressure during each course of treatment, which is set by the assigned physician. Monoblock single place chambers typically use a pressure of 1.5 to 3.0 ATA.
In general, the single cabin window is made of see through acrylic enabling to watch outside, also the patient can communicate with the technician through the internal audio system, who always monitors the patient from the outside of the cabin. Single place chamber is commonly used in hospitals and private office environments. It can treat 14 different diseases with FDA approval.
Monoblock multiple place chamber
Multiple place chambers are constructed to accommodate more than one patient at a time…
Read MoreThe size of the cabin varies greatly, from two people to eight, twelve or even twenty-four. Given the size of these chambers, they are pressurized with conventional indoor air, and each patient wears a special mask or head mask to breathe 100% oxygen.
All patients treated at the same time will be treated at the same atmospheric pressure, so patients are usually grouped according to their condition. The maximum pressure in the multiple place room can reach 6 ATA. In the cabin, according to their condition and cabin configuration, patients can sit on a bench or personal chair or recliner during the treatment, and can be accompanied by hyperbaric
technicians together with other patients. In addition, internally, many multi-function rooms will be equipped with a TV for patient entertainment, and all patients can watch the same content. Multifunctional rooms can be found in private office centers, but are more common in hospitals or trauma centers.
Monoblock mild chamber
Compared with the other two types mentioned above, the structure, configuration and …
Read Morecapacity of mild hyperbaric cabin are different. A mild chamber is often referred to as a “soft” chamber because the material used to make the chamber shell are usually canvas or elastic plastic. The mild room is only approved by FDA for the temporary treatment of acute mountain sickness, and is pressurized with indoor air up to 1.3 ATA or 10 feet below sea. Unlike the other cabins that use 100% oxygen, patients in mild cabins breathe compressed air. Due to the limited pressure and the use of compressed air instead of 100% oxygen, the application range of mild hyperbaric chamber is more limited.
Hyperoxia
Hypoxia in hyperbaric chamber angiogenesis
This mechanism is possible because when hyperbaric oxygen is given, the concentration …
Read Moreof dissolved oxygen in blood increases 20 times, and the gas combined with hemoglobin is quickly replaced by oxygen in carbon monoxide. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen treatment is about 5 times that of wearing oxygen mask under atmospheric pressure.
However, the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy is not limited to the cure of carbon monoxide poisoning. Recently, the effects of increasing tissue resistance to infection, inhibiting toxin production and promoting wound healing have been confirmed.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (referred to as HBOT) may not be familiar to the general public, but it uses hyperbaric oxygen therapy instrument to inhale pure oxygen in a high-pressure environment. It is an oxygen therapy that increases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood and improves tissue in low-pressure state. In addition, due to the toxicity of oxygen, it helps to treat wounds in difficult situations by activating the bactericidal ability of leukocytes, promoting angiogenesis, reducing edema and enhancing the bactericidal effect of antibacterial agents.
How are blood vessels created?
As an aorta, blood vessels leave the heart, branch off and become thinner, into …
Read Morecapillaries, distribute throughout the body, provide oxygen and nutrition for the tissue, and then return to the heart as veins. When the mother develops foetation, these blood vessels begin to form first. Without blood vessels, embryos cannot develop, and even organs such as liver and pancreas cannot form. In addition, as the saying goes, “people get older with their blood vessels”, therefore atherosclerosis progresses with age, leading to myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction and other diseases. Thereby it’s obvious the importance of blood vessels.
The body has a special mechanism to produce blood vessels. A typical example is a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are many kinds of growth factors acting on various cells, but VEGF is a growth factor that selectively acts on vascular endothelial cells that make up blood vessels. When there is not enough oxygen to differentiate from the cells that form the basis of blood vessels (stem cells) into vascular endothelial cells, VEGF will be produced, which also acts on vascular endothelial cells to produce new blood vessels.
VEGF also plays a central role in adult angiogenesis, such as endometrium and wound healing. Cancer also uses this mechanism to produce blood vessels. In other words, cancer cells sense hypoxia and produce a large amount of VEGF, but due to gene mutation caused by synergy, the expression of VEGF gene will increase no matter how hypoxia is.
Research findings
In laboratory, experiments are focused on the vascular endothelial cells that make up…
Read Moreblood vessels and studies the regulation of gene expression in vascular endothelial cells during angiogenesis. So far, the research on the transcription factors expressed by vascular endothelial cells (factors regulating gene expression) has clarified the transcription factors that promote and inhibit angiogenesis. Also it has identified the target gene of the gene and analyzed its function. In addition, the research isolated and identified the molecules required for angiogenesis from the genes whose expression fluctuated during the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into vascular endothelial cells, and analyzed their functions. At the moment, special attention is focused on “angiostatin”, a new factor which was found that vascular endothelial cells express themselves and regulate angiogenesis in an inhibitory manner.
Let’s explain it again. The body has a mechanism to control when certain stimuli occur so that the stimuli are not too excessive. Hormone secretion is well-known. When hormones work, if there is too much hormone, it will cause harm to the body. Therefore, negative feedback mechanism is used to control the release and function of hormones. It is hypothesized that there may be a similar regulatory mechanism in angiogenesis, and comprehensively analyzed the fluctuating genes of vascular endothelial cells stimulated by VEGF. As a result, scientists found a new factor controlling angiogenesis and named it bazohibin.
Bazohibin is a protein produced by vascular endothelial cells during angiogenesis. It is a factor that acts on itself and inhibits angiogenesis. Scientists are conducting research and believe that the growth and metastasis of cancer can be controlled by using bazohibin.
What is angiogenesis?
Angiogenesis is the physiological function of the body which generates new blood…
Read Morevessels (Figure 1). In adults, it occurs in the endometrium, depending on the sexual cycle or when the wound heals due to injury (wound healing), but in addition, angiogenesis usually does not occur. The fact that angiogenesis occurs as needed in a limited area means that, in other words, there is a control mechanism to prevent unnecessary formation of blood vessels.
However, cancer is a representative of diseases in which this control mechanism has failed. Cancer has no blood vessels. Without blood vessels, there is not enough oxygen and nutrients, so cancer cannot exceed a certain size (2-3 m3). As a result, cancer creates new blood vessels (tumor vessels) and draws blood from the surrounding vessels. Once blood vessels are formed, the cancer becomes larger (advanced cancer) and metastases throughout the body (Figure 2). In other words, stopping angiogenesis and making cancer a siege may help cure it.
Figure 1 / angiogenesis
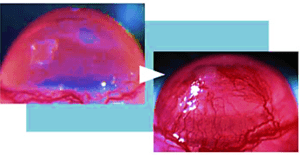
Angiogenesis and disease relationship
Cancer is the representative of angiogenesis related diseases, accounting for about 30%…
Read Moreof the causes of death in Japan, but cancer is not the only angiogenesis related disease. Together with cancer, atherosclerosis is an important disease in developed countries, including Japan. About 30% of Japanese died of cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction caused by atherosclerosis, but myocardial infarction is the primary cause of death in European and American countries.
In fact, angiogenesis is also largely involved in this atherosclerosis. The great arteries have blood vessels that supply the arteries from the outside. In atherosclerosis, this nourishing blood vessel will lead to angiogenesis, which will aggravate atherosclerosis. In addition, although it is not a direct cause of death, angiogenesis is closely related to diabetic retinopathy, rheumatoid arthritis and other serious sequelae.
As for diseases, it only emphasizes the bad side of angiogenesis, but there are also good sides. Collateral circulation (bypassing blood vessels) occurs when arteries may be blocked, but angiogenesis is also important here. So far, surgery is the only treatment for poor collateral circulation, but now, revascularization therapy to promote angiogenesis and form collateral circulation is being tried.
Lastly
Angiogenesis is closely related to cancer and atherosclerosis, which account for…
Read Moremore than half of the causes of death in Japan. Because the uncontrolled angiogenesis leads to the progress of these diseases, it is expected to establish an effective treatment to control angiogenesis.
Cancer, in particular, is difficult to cure with one treatment, and must be treated intensively by various means. In addition to surgery, radiotherapy and anticancer drugs, antiangiogenic drugs are also used in combination. It is expected that if treated, the treatment effect will be significantly improved. Anyway the researches should continue to find the useful treatment of diseases.
What is HBOT ? Effects of HBOT
Research findings
This is a treatment that attempts to improve the body condition by inhaling oxygen …
Read Morein a pressure environment above normal atmospheric pressure. The amount of oxygen we get from unconscious breathing is almost constant. Oxygen inhaled through breathing is carried into the blood and delivered to the whole body. However, disease or injury can narrow and block blood vessels. If the blood flow is damaged and oxygen is difficult to reach, the cells will be damaged and their function will decline. When inhaling oxygen in the environment with high atmospheric pressure, it can bring oxygen into the body, up to about 10 times the amount of oxygen obtained by breathing under normal atmospheric pressure. Inhale a large amount of oxygen into the body to reach the tips of the limbs and improve all hypoxia conditions. Because it plays a role in angiogenesis and tissue repair, it also promotes wound healing.
High pressure oxygen device
There are two types of hyperbaric oxygen treatment equipment for hyperbaric oxygen treatment: type 1 equipment and type 2 equipment. Our company has first-class equipment.
Type 1 equipment (1 person)
It is a device that can hold a patient in a tank and pressurize it with 100% oxygen for treatment. Since the equipment is filled with 100% oxygen, there are many restrictions on items that can be brought into the tank, such as items that may catch fire or items that cannot withstand pressure. During the treatment, the pressure was raised to 2 atmospheres and treated for 60 minutes.
Effect of high pressure
The volume of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure, and the amount of …
Read Moredissolved gas is directly proportional to the pressure. Therefore, when the pressure is high, the volume of gas in the body (in blood vessels) decreases and the gas in the body (in blood vessels) dissolves in blood and body fluids. As a result, it is expected to improve circulatory disorders.
Process flow
- pre questionnaire
- physical examination (preliminary examination possible)
- interpretation and consent of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- change into a special dress (100% cotton) to prepare for treatment
- the nurse will check your symptoms and check your belongings and clothing.
- move to hyperbaric oxygen treatment room
- a clinical engineer will explain ear removal and check clothes and belongings (carefully).
- enter the device and start treatment.
- treatment time (90-120 minutes)
Fill the treatment equipment with 100% oxygen (about 6 minutes)
- time from atmospheric pressure rise to treatment pressure (about 15 to 30 minutes)
- time to maintain treatment pressure (60 minutes)
- time from treatment pressure to atmospheric pressure (about 15 to 30 minutes)
- end of treatment
Effects of HBOT
Oxygen in the blood binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells and is carried in the form of …
Read More“bound oxygen”. Therefore, even if 100% oxygen is inhaled, the upper limit of oxygen that can be combined with hemoglobin is set. However, this is a treatment method aimed at improving the disease by applying high pressure to dissolve oxygen directly in the liquid components of the blood to increase the amount of “dissolved oxygen”.
Increasing the amount of dissolved oxygen by applying pressure is expected to produce the following effects.
Effect of high concentration oxygen
Through the intake of high concentration oxygen, dissolved oxygen increases and a large…
Read Moreamount of oxygen is transported around, so it is expected to improve hypoxia and circulatory disorders.
Indications
- decompression sickness or air embolism
- acute carbon monoxide poisoning and other gas poisoning (including intermittent type)
- severe soft tissue infection (gas gangrene, necrotizing fasciitis) or intracranial abscess
- acute peripheral vascular disease
(B) severe burns or frostbite
(C) peripheral vascular disease with extensive contusion or moderate or high vascular rupture
(D) compartment syndrome or crush syndrome
- cerebral infarction
- severe head injury or disturbance of consciousness or brain edema after craniotomy
- severe hypoxic encephalopathy
- intestinal obstruction
- central retinal artery occlusion
- sudden deafness
- malignant tumors in combination with radiation or anticancer drug therapy
- peripheral circulation disorder with intractable ulcer
- skin transplantation
- spinal nerve diseases
- osteomyelitis or radiation injury
Precautions during treatment
- Ear pressure removal
At the beginning of treatment, you may feel…
Read Moreear pain or blockage. If this happens, do one of the following:
- hold your nose and swallow saliva
- close your mouth, hold your nose and blow your nose
- through these methods, you will feel the air flowing out of your ears, and you will get rid of the pain and blockage of your ears.
- What can you bring
Since 100% oxygen is used to increase the pressure, you cannot bring anything that may catch fire or be damaged by pressure into the equipment you are using. When receiving hyperbaric oxygen treatment, do not carry the following items with you.
Things that may become a source of ignition (various warmers, matches, lighters, cigarettes, etc.)
- items with fire hazard (manicure, celluloid, grease, etc.)
- items (mobile phones, hearing aids, watches, keys, etc.) that are sparked by impact and damaged by pressure
- Clothing
- during hyperbaric oxygen treatment, please change into 100% cotton clothes (please wear 100% cotton underwear to reduce static electricity).
History of HBOT 1662
Since 1662

The first use of HBOT was recorded in 1662. A British doctor developed a residence, the first hyperbaric oxygen chamber. However, it was not until the 1800s that hyperbaric oxygen therapy laid the foundation. French engineer, doctor and scientist Paul Burt wrote LA pressure barometrique in 1872.
The first hyperbaric oxygen chamber in the United States was built by Dr. J. Leonard Corning in New York in 1891.
Corning’s interest in HBOT stems from witnessing the severe decompression sickness of workers at the Hudson tunnel site. They often have severe muscle pain and paralysis after working below sea level for a whole day. This is also a well-known phenomenon in bridge construction, the most famous of which is the Brooklyn Bridge in 1889.
Shortly after, Dr. Orval Cunningham, director of Anesthesiology at University of Kansas School of medicine, observed that the incidence rate and mortality rate of the 1918 Spanish flu epidemic were higher in high altitude areas. The use of high-pressure cabin in the influenza pandemic was studied than in coastal areas, he attributed to atmospheric pressure.
In the 1930s and 1940s, the U.S. Navy began to study the use of HBOT to treat deep-sea divers with decompression sickness. Twenty years later, this treatment was also widely known for treating carbon monoxide poisoning.
In 1967, the society of undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine (UHMS) was established. UHMS is an international non-profit association serving about 2000 doctors, scientists, colleagues and nurses in the field of high-pressure and diving medicine from more than 30 countries. In addition to serving as an important source of scientific and medical information related to hyperbaric medicine through its bimonthly, peer-reviewed journals, symposiums, courses, certifications and seminars, UHMS also puts forward policy guidelines and advocates in various settings, including new uses and applications.
Today, HBOT is used to treat a variety of diseases. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved 14 diseases treated with HBOT. This set of conditions is usually covered by insurance, but specific qualifications for each condition need to be met (please consult your insurance company to confirm the coverage of your plan). However, many studies support the effectiveness of HBOT in the treatment of many other indications, and many countries around the world have approved it for more than 50 different diseases.
Application of hyperbaric oxygen treatment module in clinical diseases
In this process, hyperbaric oxygen therapy began to be important in clinical application. In 1955, WH Brummelkamp, J. Hendrik and I. Boerema (1961) used hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) to treat anaerobic infection and open heart surgery at Amsterdam Medical University. In 1960, i. Boerema and his colleagues published “life without blood”, in which even if the red blood cells of pigs were removed during hyperbaric oxygen injection, there were no adverse reactions in pigs. This is an opportunity to stimulate the desire for new treatment. The concept of using a small room sized high-pressure chamber for open heart surgery has been introduced. Some private hospitals have begun to introduce several large high-pressure chambers. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in surgery is very disappointing, and it is very rare to use it for this purpose. In the 1960s, the concept of single chamber 100% oxygen therapy was introduced into radiotherapy for cancer patients. On the other hand, reports at the first and second international conferences on hyperbaric oxygen held in Amsterdam in 1963 showed that HBO had a significant effect on clostridial muscle necrosis and carbon monoxide poisoning (Brummelkamp et al., 1961 and Douglas et al., 1964)
In 1965, the U.S. Air Force hyperbaric oxygen treatment team reported that gas gangrene or carbon monoxide poisoning could be well treated if diagnosed and treated at the same time, even if it would be life-threatening (Davis et al. 1973).
In the 1970s, the role of HBO decreased to chronic refractory osteomyelitis (depenbusch 1972), radiation osteonecrosis of the maxillofacial region (mainous and Boyne 1974), osteogenic enhancement of bone grafts (mainous et al. 1973), and preservation of skin grafts, PERRINS 1970) and proved its effectiveness in the treatment of chronic incurable soft tissue wounds (niinikoski 1969).Evolution of chamber safety regulations
The progress of hyperbaric oxygen therapy has opened up a new medical field. It also reconsidered its view on safety. Depending on the patient, equipment for indoor treatment or treatment is required, such as ECG, defibrillator, inhaler, arterial blood analyzer and other life support equipment. Warnings and concerns about the general safety of clinical room design and operation can be found in some literature (Boerema 1965; brown and Smith 1965; meijne 1973). New potential hazards include communication equipment, fire hazards, mechanical damage, oxygen poisoning and decompression sickness. These warnings were not just warnings, but a series of fatal fires occurred one after another, including a fatal fire on an experimental submarine of the U.S. Navy in 1965 and 100% oxygen in 1967. Apollo command fire accident module. There are many studies on accident causes and environment. According to the reports of 11 fire accidents in the cabin, 7 occurred in the high-pressure cabin, the environment is rich in oxygen, and most of them ignore the power supply (Alger and Nichols 1971). Therefore, the safety design of the chamber is mainly concerned to protect patients or chamber personnel. In order to prevent fire accidents, he began to pay special attention to the fire extinguishing system and formulated a series of safety regulations. In 1968, the U.S. Navy took the lead in introducing the cabin safety qualification system for U.S. Navy personnel (U.S. Navy, 1973). Other groups have also begun to institutionalize safety regulations for high-pressure installations: Compressed Gas Association (1966), National Fire Protection Association (1970), U.S. Department of labor, Department of occupational safety and health (1977). It can be said that the OSHA standard (1977) of the U.S. Department of labor fully reflects the concern of the U.S. government for indoor safety.
Design and installation standards for pressure vessels already exist. According to the building code of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), a physically safe room can be built. Recently, the ASME Code began to include the design and construction of pressure chambers for human habitation. Moreover, most of these cavities are made in the United States and are manufactured in strict accordance with ASME safety regulations. Similar provisions exist in Europe, represented by DET Norske Veritas. Now every country has regulations on cabin safety, such as Lloyd’s register of shipping regulations and Korea classification society regulations.
In order to treat the casualties caused by deep-sea diving, various modifications have been made to the high-pressure chamber,
To expand hyperbaric oxygen therapy, doctors must know the basic principle of how the cabin works.
MEDICAL HYPERBARIC SOLUTIONS
Office Address
Romania
Contact Us
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +40 742 112 575
